- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
JOURNEY BEGINS
Welcome to the blog of Errolee Gerie.✋✋

.
Media literary
eye color changing was the first activity that we have done in this course.
Binary code
We learn how to convert any number into binary code which is the language of our DEAR computer. The short video below will show you how we covert:
hope you enjoy the video and that it was useful
as a reminder, we decide by 2 because binary starts with bi=2.
Moreover, I know you all want a realistic picture without spending hours on taking the RIGHT PICTURES with the RIGHT ANGLE. I got guys to watch that youtube video and I promise you will spend fewer hours editing.
- CamStudio at this time only supports Windows and has very little in the way of editing capabilities unless you can install some of the user-made extensions.
- With no base editing capabilities, the software is really stripped down when compared to some of the competitors and it cannot directly record for mobile devices without a patch.
- It's also not a great program for game recording and it only offers output formatting SWF and AVI.
- The official website has also had some problems with security from individuals downloading software extensions infected with Trojan viruses.
More and more companies are looking at a CAVE system VR when they want to be able to bring several people into a single virtual experience. The ability to have up to 10 people all watching the same image, with one person acting as leader or guide through the virtual experience makes it great for a group, especially in a presentation-type scenario. As well as having people in front of the screen, several remotely located CAVE virtual reality systems can be connected together to provide a collaborative experience, even adding in remote users with Head Mounted Displays (HMDs) as avatars on the screen.
Does the CAVE automatic virtual environment have limits?
There can be many obstacles to the adoption of the VR CAVE, starting with the cost of installation. This type of immersive 3D installation costs around €80,000 for a 2-sided corner cave and up to €750,000 for a 6-sided CAVE, plus the maintenance and usage costs that can amount to more than €3,000 per month.
The space required is also a vital consideration in the installation of a CAVE virtual environment. It is imperative to have a relatively spacious room to accommodate all the needed hardware (the TORE project illustrates this well), and the necessary space for the installation of projectors (which is less in the case for LED screens or when using mirrors), plus items such as the air conditioning system, lighting, control desk, etc.
The installation of a virtual reality CAVE also has several factors to consider to ensure optimum performance, for example, a strong vibration close to the cave automatic virtual environment can shift the projectors and force a resynchronization or an external light source can interfere with the tracking.
Augmented reality
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Types of Recommender Systems
Recommender systems are typically classified into the following categories:
- Content-based filtering
- Collaborative filtering
- Hybrid systems
Depending on whether a model is learned from the underlying data, recommender system can be divided into:
- Memory-based
- Model-base
A Movie Recommendation Example
Consider a movie recommendation system in which the training data consists of a feedback matrix in which:
- Each row represents a user.
- Each column represents an item (a movie).
The feedback about movies falls into one of two categories:
- Explicit— users specify how much they liked a particular movie by providing a numerical rating.
- Implicit— if a user watches a movie, the system infers that the user is interested.
To simplify, we will assume that the feedback matrix is binary; that is, a value of 1 indicates interest in the movie.
When a user visits the homepage, the system should recommend movies based on both:
- similarity to movies the user has liked in the past
- movies that similar users liked
Advantages
No domain knowledge necessary
We don't need domain knowledge because the embeddings are automatically learned.Serendipity
The model can help users discover new interests. In isolation, the ML system may not know the user is interested in a given item, but the model might still recommend it because similar users are interested in that item.Great starting point
To some extent, the system needs only the feedback matrix to train a matrix factorization model. In particular, the system doesn't need contextual features. In practice, this can be used as one of multiple candidate generators.
Disadvantages
Cannot handle fresh items
The prediction of the model for a given (user, item) pair is the dot product of the corresponding embeddings. So, if an item is not seen during training, the system can't create an embedding for it and can't query the model with this item.
Hard to include side features for query/item
Side features are any features beyond the query or item ID. For movie recommendations, the side features might include country or age. Including available side features improves the quality of the model. Although it may not be easy to include side features in WALS, a generalization of WALS makes this possible.
Content-based Filtering
Content-based filtering uses item features to recommend other items similar to what the user likes, based on their previous actions or explicit feedback.
You also represent the user in the same feature space. Some of the user-related features could be explicitly provided by the user. For example, a user selects "Entertainment apps" in their profile. Other features can be implicit, based on the apps they have previously installed. For example, the user installed another app published by Science R Us.
The model should recommend items relevant to this user. To do so, you must first pick a similarity metric (for example, dot product). Then, you must set up the system to score each candidate item according to this similarity metric. Note that the recommendations are specific to this user, as the model did not use any information about other users.
Content-based Filtering Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages
- The model doesn't need any data about other users, since the recommendations are specific to this user. This makes it easier to scale to a large number of users.
- The model can capture the specific interests of a user, and can recommend niche items that very few other users are interested in.
Disadvantages
- Since the feature representation of the items are hand-engineered to some extent, this technique requires a lot of domain knowledge. Therefore, the model can only be as good as the hand-engineered features.
- The model can only make recommendations based on existing interests of the user. In other words, the model has limited ability to expand on the users' existing interests.
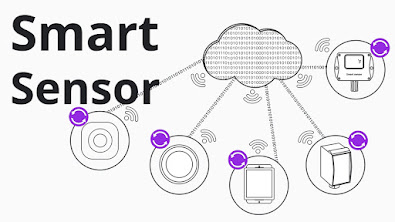
What is Smart System
What is a smart sensor?
A smart sensor is a device that takes input from the physical environment and uses built-in compute resources to perform predefined functions upon detection of specific input and then process data before passing it on.
Smart sensors enable more accurate and automated collection of environmental data with less erroneous noise amongst the accurately recorded information. These devices are used for monitoring and control mechanisms in a wide variety of environments including smart grids, battlefield reconnaissance, exploration and many science applications.
The smart sensor is also a crucial and integral element in the internet of things (IoT), the increasingly prevalent environment in which almost anything imaginable can be outfitted with a unique identifier and the ability to transmit data over the internet or a similar network. One implementation of smart sensors is as components of a wireless sensor and actuator network (WSAN) whose nodes can number in the thousands, each of which is connected with one or more other sensors and sensor hubs, as well as individual actuators.
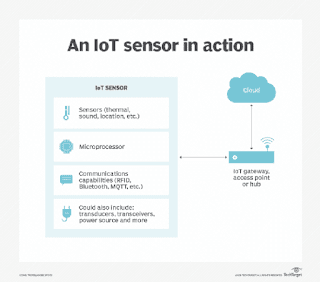
Compute resources are typically provided by low-power mobile microprocessors. At a minimum, a smart sensor is made of a sensor, a microprocessor and communication technology of some kind. The compute resources must be an integral part of the physical design -- a sensor that just sends its data along for remote processing isn't considered a smart sensor.
How do smart sensors work?
A smart sensor ties a raw base sensor to integrated computing resources that enable the sensor's input to be processed.
The base sensor is the component that provides the sensing capability. It might be designed to sense heat, light or pressure. Often, the base sensor will produce an analog signal that must be processed before it can be used. This is where an intelligent sensor's integrated technology comes into play. The onboard microprocessor filters out signal noise and converts the sensor's signal into a usable, digital format.
- ethical guidelines are a set of principles or rules that help individuals or organizations make decisions in a morally responsible and fair manner. They serve as a roadmap for behavior and decision-making, helping to ensure that people act in accordance with their values and obligations. Some common ethical guidelines include:
- Honesty: Being truthful and transparent in all dealings and interactions.
- Respect: Treating others with dignity and courtesy, regardless of their background or beliefs.
- Responsibility: Being accountable for one's actions and decisions and taking ownership of the consequences that arise from them.
- Fairness: Treating others equally and without bias and avoiding any actions that would be seen as discriminatory or unjust.
- Confidentiality: Protecting sensitive information and respecting the privacy of others.
- Professionalism: Maintaining high standards of competence, skill, and integrity in one's work.
- Sustainability: Ensuring that actions and decisions consider their impact on the environment and future generations.
- These ethical guidelines can be found in many different settings, including businesses, professions, and organizations, and they help to promote integrity, trust, and social responsibility.
- Do not cause harm - As stated in the first principle of the IEEE Code of Ethics for Engineers, individuals should not participate in or knowingly allow the use of technology that causes harm to individuals or the environment.
- Respect privacy - The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) and the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) both recognize the right to privacy as a fundamental human right.
- Use technology for the greater good - The ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct states that individuals should use technology to promote the general welfare of society and its members.
- Be transparent - The IEEE Code of Ethics for Engineers emphasizes the importance of transparency in the development and use of technology.
- Uphold fairness - The IEEE Code of Ethics for Engineers states that individuals should avoid discrimination and promote fairness in the use of technology.
- Avoid creating or perpetuating inequality - The ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct states that individuals should strive to avoid creating or perpetuating inequality through their work.
- Respect intellectual property rights - The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) recognizes the importance of protecting the rights of creators and innovators.
- Promote digital literacy and educate others - The ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct stresses the importance of education and digital literacy as a means of promoting responsible technology use.
- Be accountable for your actions - The IEEE Code of Ethics for Engineers requires individuals to be accountable for their work and to accept responsibility for the impact of their technology choices.
- Continuously reflect on and improve your ethical standards - The ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct encourages individuals to continuously reflect on and improve their ethical standards as they engage with new technologies and ethical challenges.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps











.png)


Comments
Post a Comment